[This post was written by Marc Jacobs and describes his MSc Thesis research]
Nowadays the world does not just rely on traditional news sources like newspapers, television and radio anymore. Social Media, such as Twitter, are claiming their key position here, thanks to the fast publishing speed and large amount of items. As one may suspect, the credibility of this unrated news becomes questionable. My Master thesis focuses on determining measurable features (such as retweets, likes or number of Wikipedia entities) in newsworthy tweets and online news articles.
The gathering of the credibility features consisted of two parts: a theoretical and practical part. First, a theoretical credibility framework has been built using recent studies about credibility on the Web. Next, Ubuntu was booted, Python was started, and news articles and tweets, including metadata, were mined. The news items have been analysed, and, based on the credibility framework, features were extracted. Additional information retrieval techniques (website scraping, regular expressions, NLTK, IR-API’s) were used to extract additional features, so the coverage of the credibility framework was extended.
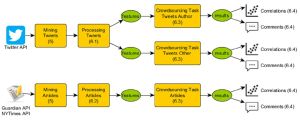
The data processing and experimentation pipeline
The last step in this research was to present the features to the crowd in an experimental design, using the crowdsourcing platform Crowdflower. The correlation between a specific feature and the credibility of the tweet or news article has been calculated. The results have been compared to find the differences and similarities between tweets and articles.
The highly correlated credibility features (which include the amount of matches with Wikipedia entries) may be used in the future for the construction of credibility algorithms that automatically assess the credibility of newsworthy tweets or news articles, and, hopefully, adds support to filter reliable news from the impenetrable pile of data on the Internet.
Read all the details in Marc’s thesis


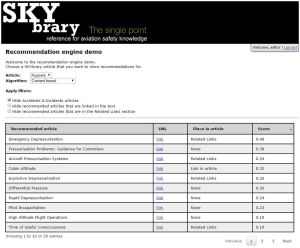
 Part of this project was a case study on SKYbrary, a knowledge portal on the subject of aviation safety. In this project I looked at the types of data that are typically available to knowledge portals. I used user navigation pattern data, which I retrieved via the Google Analytics API, and the text of the articles to create a user-navigation based and a content based algorithm. The user-navigation based algorithm uses an item association formula and the content based algorithm uses a tf-idf weighting scheme to calculate content similarity between articles. Because both types of algorithm have their separate disadvantages, I also developed a hybrid algorithm that combines these two.
Part of this project was a case study on SKYbrary, a knowledge portal on the subject of aviation safety. In this project I looked at the types of data that are typically available to knowledge portals. I used user navigation pattern data, which I retrieved via the Google Analytics API, and the text of the articles to create a user-navigation based and a content based algorithm. The user-navigation based algorithm uses an item association formula and the content based algorithm uses a tf-idf weighting scheme to calculate content similarity between articles. Because both types of algorithm have their separate disadvantages, I also developed a hybrid algorithm that combines these two.